
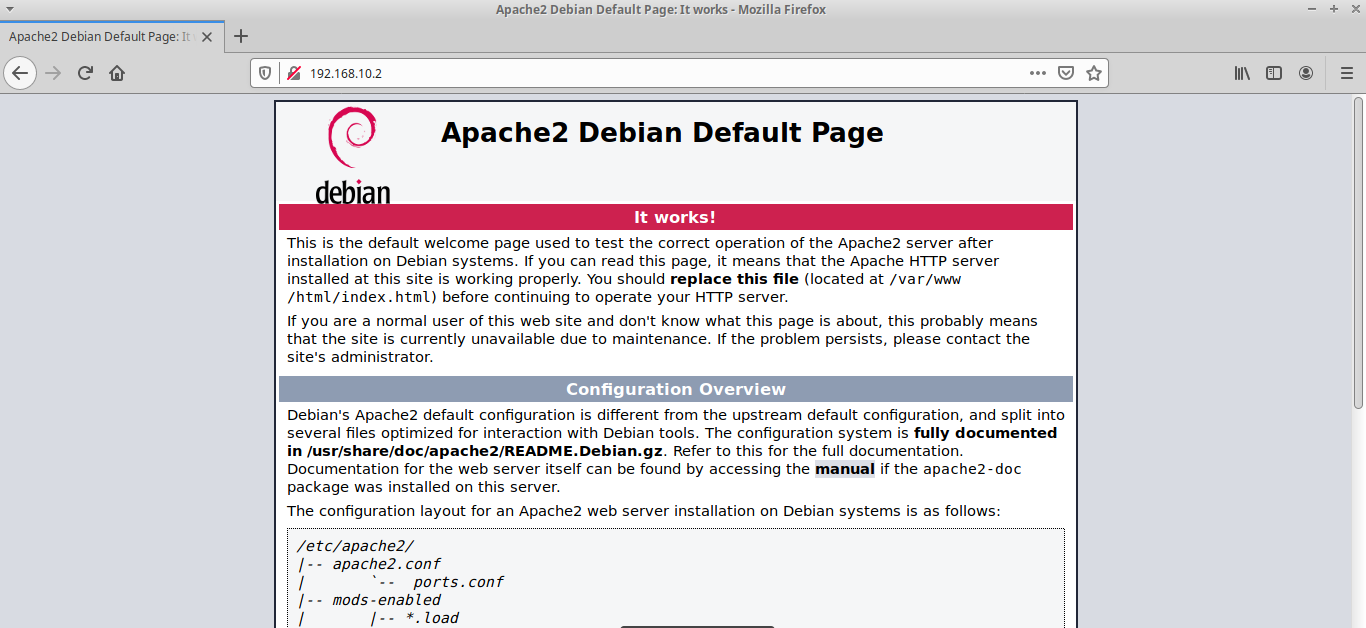
You should see “It works!” Web page, which means Apache Web server is running properly. Now type in the public IP address of your Debian 9 server in the browser address bar. Output: Server version: Apache/2.4.25 (Debian) It’s also a good idea to enable Apache to automatically start at boot time. If it’s not running, use systemctl to start it. Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/rvice enabled vendor preset:Īctive: active (running) since Sun 02:36:48 UTC 5min ago sudo apt install apache2 apache2-utilsĪfter it’s installed, Apache should be automatically started. The apache2-utils package will install some useful utilities like Apache HTTP server benchmarking tool (ab). Sudo apt upgrade Step 2: Install Apache Web ServerĮnter the following command to install Apache Web server. Run the following command on your Debian 9 OS. Step 1: Update Software Packagesīefore we install the LAMP stack, it’s a good idea to update repository and software packages.
You can add sudo at the beginning of a command, or use su - command to switch to root user. Please note that you need to have root privilege when installing software on Debian. You can follow this tutorial on a VPS (Virtual Private Server) or on a local Debian 9 computer. However, since MySQL is now owned by Oracle and there’s a chance that Oracle turns it to a closed-source product, we will choose MariaDB instead of MySQL.

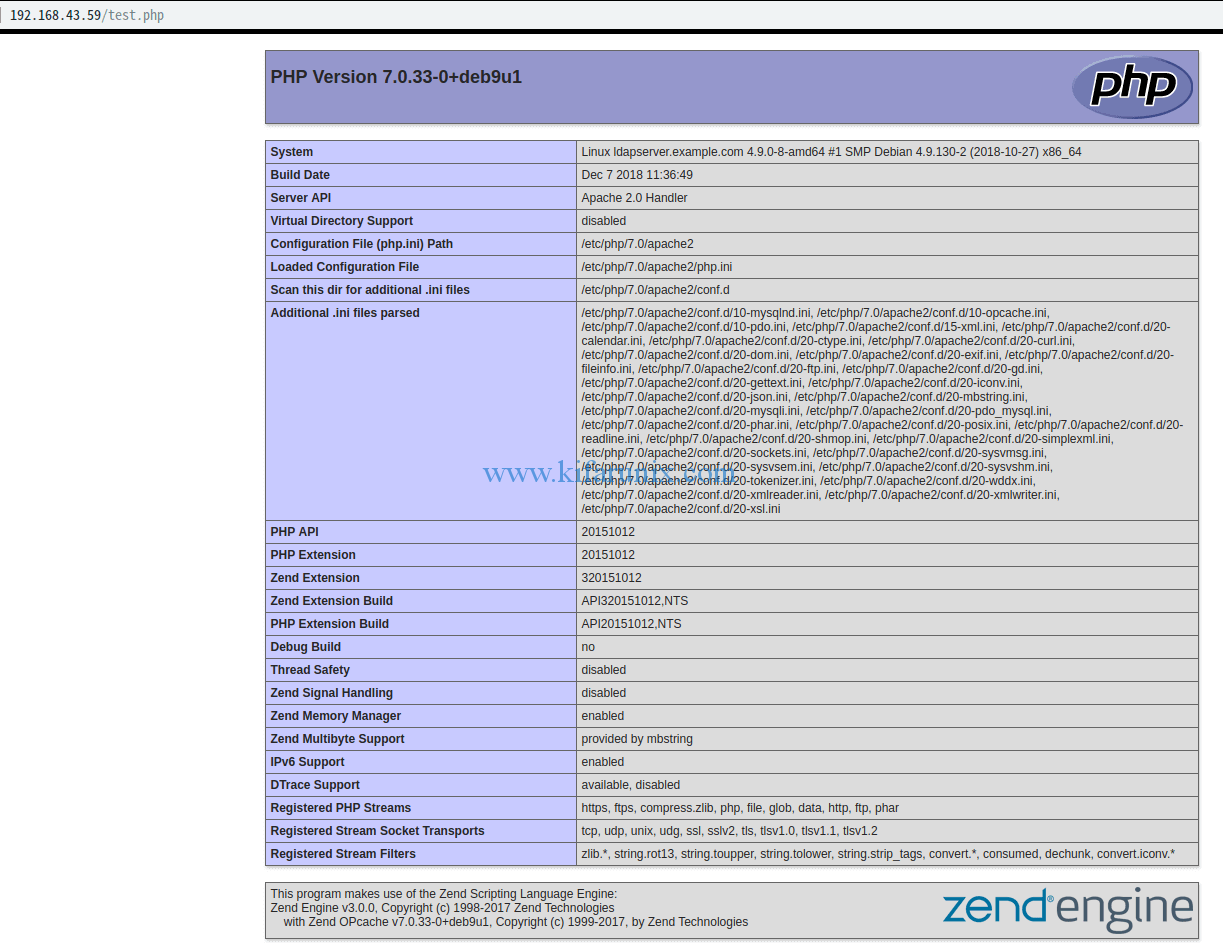
It’s made up of four components – Linux, Apache, MySQL/ MariaDB, PHP – Linux is the operating system Apache is the web server MySQL/MariaDB is database PHP is a server-side scripting language.Īll of the four components are free and open-source. This tutorial is going to show you how to install Apache, MariaDB and PHP7 (LAMP stack) on Debian 9 stretch. LAMP is the most common web service stack for building dynamic websites and web applications.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
